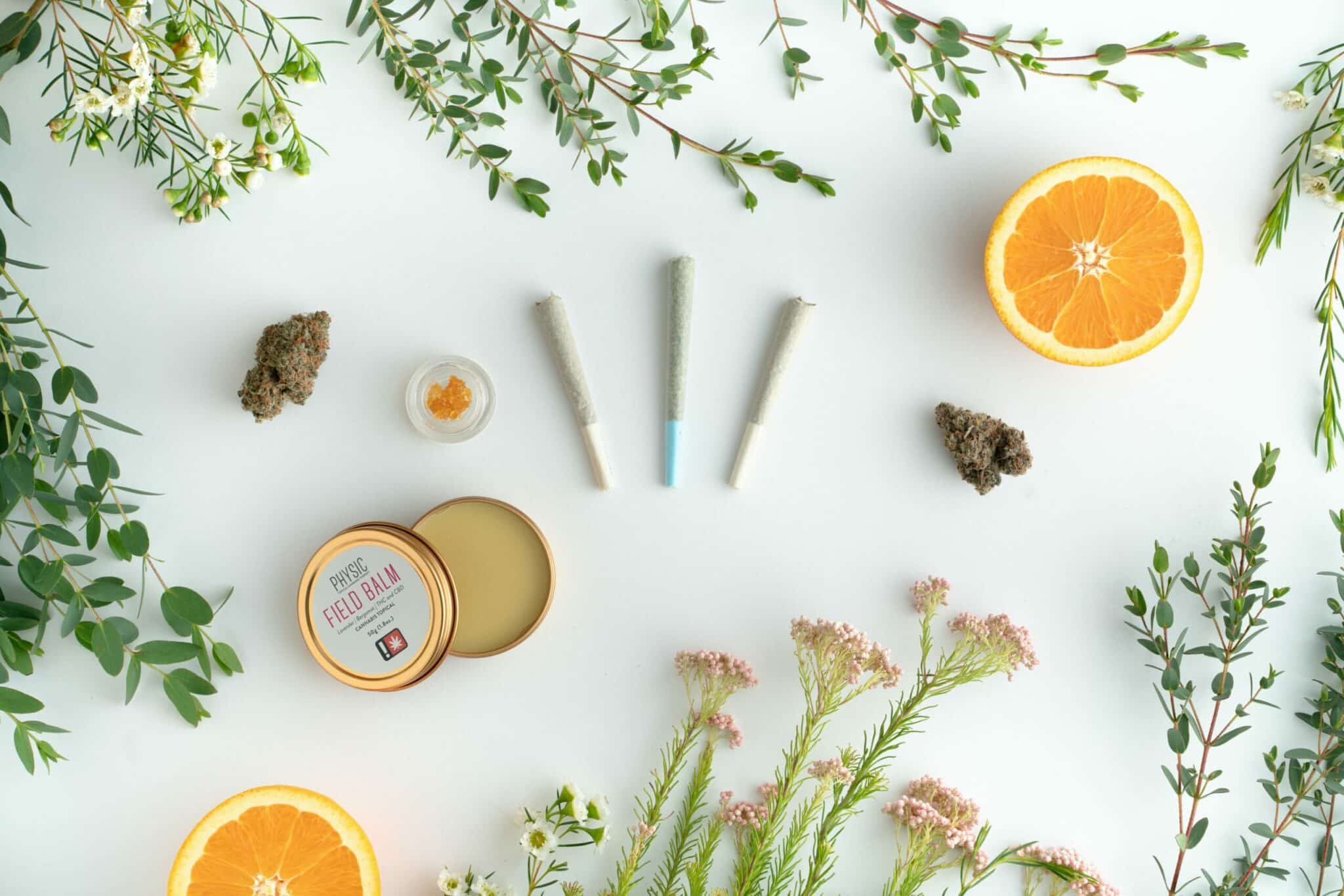
What are terpenes? Why are they beneficial in CBD products?
Do cannabis strains like Lemon Haze or Buddah Cheese really contain lemon or cheese? Of course not. But then, how to explain the sometimes striking differences in flavor between two hemp varieties?
As the title suggests, these variations are due to the terpenes present in plants. But what are terpenes, what are they used for, and how do they work? These are just some of the questions Canna-House will be answering in this article.
What are they?
Terpenes are molecules with odoriferous properties, produced by many plants. Simply put, they give plants their scent and flavor.
They are found in various natural substances such as oils, hormones, vitamins and cannabinoids. In everyday life, they are found in a multitude of products including essential oils, foods, cosmetics and household products, among others.
Terpenes are actually natural hydrocarbons, often considered essential oil extracts for simplicity’s sake. They are produced naturally by plants, including cannabis, as well as by other plant species such as conifers (e.g. firs). They can also be found in certain living species, such as insects and even marine sponges.
What are they for?
As is the case with many other plants, this plant mechanism has been developed to help the plant defend itself by repelling harmful insects and attracting those beneficial to its pollination.
How do they work?
In addition to offering exceptional and varied flavors, terpenes also play an important role in amplifying the effects of other cannabinoids.
It’s only very recently that research has begun to take a close interest in these hydrocarbons, mainly since their synergy with other cannabis components has come to light, a phenomenon known as the entourage effect.
Today, there are around a hundred different terpenes, including myrcene, limonene and pinene, all well known in the fields of aromatherapy and alternative medicine.
The most important terpenes in cannabis:
Here’s a summary of the main terpenes present in cannabis, their characteristics and their effects on the human body.
- Myrcene:
Myrcene is found in high concentrations in the cannabis plant.
It gives off a musky, herbaceous aroma.
Effects: accelerates the effects of cannabinoids, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, relaxing.
Other sources: wild thyme, hops, lemongrass, mango, cardamom.
- Limonene:
As its name suggests, limonene is a terpene with a characteristic citrus aroma.
It is often found in fruit peels and in a wide range of citrus fruits.
Effects: stimulating, relaxing, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory.
Other sources: citrus fruits, rosemary, conifers.
- Pinene:
Pinene is the most abundant terpene in nature.
It has a characteristic pine aroma and can be found in a wide variety of plants.
Effects: anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, anxiety
Other sources: pine, conifer resin, citrus, basil, parsley.
- Caryophyllene:
Caryophyllene is the only terpene that acts as a cannabinoid.
It binds to receptors in the brain and acts as an antioxidant.
It has a spicy, peppery aroma.
Effects: anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, relaxant, neuroprotective.
Other sources: black pepper, cloves, rosemary, hops
- Terpinolene:
Terpinolene is widely used in perfumery for its complex pine and herbal fragrance.
Effects: stimulant, anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, antioxidant
Other sources: allspice, parsnip, apple, cumin, sage, rosemary.
- Humulene:
The characteristic herbal odor of humulene is the source of beer’s hoppy aroma.
Effects: anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, appetite suppressant
Other sources: hops, coriander, basil
- Linalool:
Linalool is the main terpene in lavender and gives off a strong floral aroma.
Effects: relaxing, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial
Other sources: lavender, mint, cinnamon
So, for optimum effect, we recommend choosing a product that combines all the cannabinoids (except THC) with the plant’s terpenes.