With the evolution of laws and the growing craze for natural alternatives, there is an increase in the production of cannabinoid-based products. While CBD is now very popular and appreciated for its many uses, other cannabinoids such as CBG and CBN remain little-known to many people.
These compounds, often considered "minor", could nevertheless play an essential role in a number of promising applications. In this article, we explore the differences between CBD, CBG and CBN, and why these substances deserve your attention.
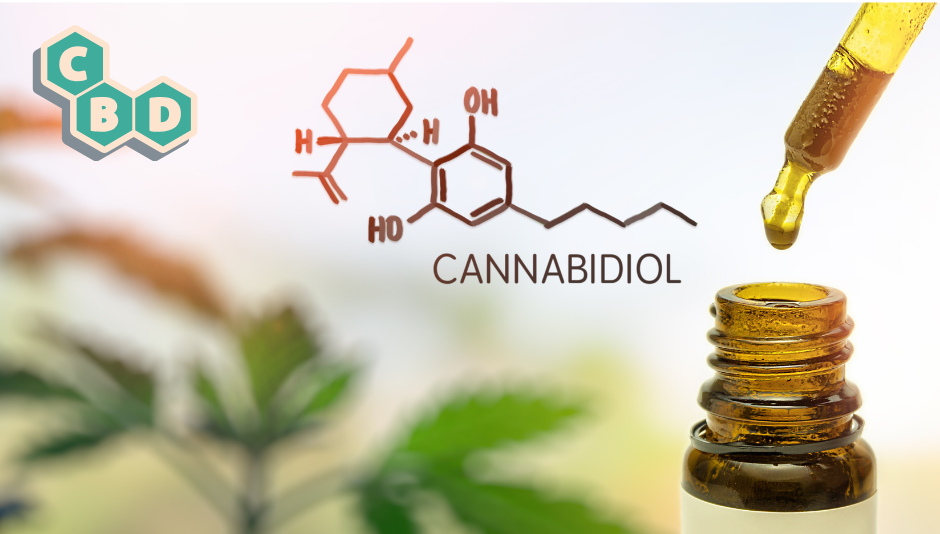
CBD (Cannabidiol)
CBD, also known as cannabidiol, is currently one of the most popular and widely used cannabinoids on the market. Its success has led to the creation of numerous specialist stores and a considerable increase in online sales. Production of this compound is mainly based on hemp plants containing less than 0.3% THC.
Unlike CBD, it has no psychoactive effects. Thanks to its ease of extraction and non-intoxicating properties, it's perfect for a wide variety of uses. What's more, no studies to date have shown any risk of addiction associated with CBD, reinforcing its reputation as a safe product.
Some benefits of CBD
Skin conditions:
CBD, when applied to the skin in oil or lotion form, may have an immediate effect. Thanks to its anti-inflammatory properties, it could be particularly beneficial for people suffering from psoriasis, acne or dermatitis.Inflammation management:
CBD is renowned for its anti-inflammatory properties, and has been shown to be effective in the treatment of pain. It could therefore be indicated for relieving pain and reducing inflammation, whether in joints or the skin.Anxiety reduction:
In addition to its analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, CBD is also said to have antidepressant properties. It is thought to promote the production of serotonin, the hormone of happiness, and may help reduce anxiety and stress.
Cannabigerol (CBG): an indispensable cannabinoid
CBG, also known as cannabigerol, is one of the many compounds found in the cannabis plant. Although less well-known than CBD or THC, it is the precursor of several other important cannabinoids, such as CBD and THC, earning it the nickname of the mother cannabinoid.
CBG is particularly present in young cannabis plants, as it has a similar molecular structure to CBD, with many of the same properties. However, its origin is different: CBG is derived from cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), which, after decarboxylation, breaks down into various other compounds such as CBDA and THCA. This makes it particularly important in the field.
CBG properties:
CBG, like other cannabinoids, has a variety of interesting properties. Among the most promising are its anti-inflammatory, therapeutic and antibacterial effects. Thanks to this wide-ranging potential, CBG could be used to alleviate a variety of ailments.Bacterial infections:
Although many bacterial infections are benign, they can lead to complications if left untreated. CBG could play a key role in this area by being able to combat bacteria resistant to conventional treatments, thus offering an effective alternative against these infections.Glaucoma:
Glaucoma is an eye disease often responsible for blindness. Research into CBG for this condition is promising. It could reduce intraocular pressure, helping to protect the optic nerve and limit the risk of damage leading to vision loss.
Cannabinol (CBN): a special cannabinoid
Scientists have studied cannabinol, also known as CBN, as the first cannabinoid. It was discovered in the late 1800s and first synthesized in 1940, and is characterized by its mode of formation: it is not naturally present in large quantities in cannabis, unlike other cannabinoids. CBN is essentially produced by the breakdown of THC, a process which accelerates with heat or time.
When combined with plants that have relaxing properties, CBN could enhance their soothing effects, making it popular with those seeking sleep assistance. What's more, this cannabinoid has other interesting properties that continue to interest scientists.
CBN, CBD and CBG are three cannabinoid compounds that interact differently with the endocannabinoid system, giving them distinct properties. Among them, CBN stands out for its slightly higher potential to induce psychoactive reactions, although these remain modest. CBD, on the other hand, has a much wider range of medical applications, thanks in part to the considerable attention it has attracted in the scientific field and the many studies devoted to it.
CBN is of particular interest for its potential to relieve chronic pain, especially in people suffering from osteoporosis or arthritis. It may also help reduce pain-induced insomnia. CBD, on the other hand, is more suited to those seeking a relaxing and soothing effect, helping to calm the mind and reduce stress.
For its part, CBG shows promise in the treatment of neurological disorders. It could also alleviate the discomfort associated with glaucoma and possesses unique antibacterial properties, capable of countering microbes resistant to conventional antibiotics. These characteristics make CBG a valuable candidate for specific medical applications, setting it apart from the other two cannabinoids.
Analysis of the combined effects of CBN, CBD and CBG
Thecombination of cannabinoids such as CBD, CBG and CBN seems to offer interesting synergistic effects, particularly when used together. For example, the combined use of CBD and CBG has been shown to be more effective than their individual use. While CBD is known for its calming and anti-inflammatory properties, CBG provides energizing effects and pain relief. Their combination can induce overall relaxation, ideal for managing pain, inflammation, anxiety and stress. This phenomenon, often attributed to the entourage effect, reflects the way in which cannabis compounds act synergistically to amplify their benefits.
These cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system in complementary ways. CBD acts primarily by modulating the production of natural endocannabinoids, while CBG binds directly to CB1 and CB2 receptors, influencing the regulation of pain and inflammation. Their combination provides a balance of effects, increasing their overall efficacy.
When CBN is added to this duo, its mild sedative properties come into play. Although research into the simultaneous use of all three compounds is still limited, preliminary studies and anecdotal feedback indicate that their combination could offer significant therapeutic benefits. For example, CBN, often used to promote sleep, could improve sleep quality when combined with CBD and CBG, notably by alleviating nocturnal pain that disrupts rest.
Some research points to the specific benefits of full-spectrum products, which include CBD, CBG, CBN and traces of THC. These products appear to maximize the individual properties of each component, offering an effective solution for reducing pain, inflammation and promoting overall well-being. In addition, it has been shown that the combination of CBN and CBD can enhance the sedative effects of CBN, making it particularly useful for people suffering from pain-related sleep disorders or insomnia.
Conclusion
Combining CBD, CBG and CBN can produce significant therapeutic effects, including pain relief, reduced inflammation, anxiety relief and improved sleep. Theentourage effect, resulting from the synergistic interaction between the different cannabinoids, reinforces the unique properties of each compound, offering a more complete and balanced approach to various health issues. However, further research is essential to deepen our understanding of the mechanisms involved and to determine optimal dosages for specific therapeutic applications.